nix CLInix develop, for example, operates on the devShells output—nothing prevents you from defining your own flake output types.
Unfortunately, such “non-standard” nix flake show and nix flake check don’t know anything about them, so they can’t display or check anything about those outputs.
The nixpkgslib output that Nix knows nothing about:
# nix flake show nixpkgsgithub:NixOS/nixpkgs/4ecab3273592f27479a583fb6d975d4aba3486fe├───...└───lib: unknownThis was a problem when we were creating
Today we’re proposing a solution to this problem: flake schemas.
Flake schemas enable flakes to declare functions that enumerate and check the contents of their outputs.
Schemas themselves are defined as a flake output named schemas.
Tools like nix flake check and FlakeHub can then use these schemas to display or check the contents of flakes in a generic way.
In this approach, flakes carry their own schema definitions, so you are not dependent on some central registry of schema definitions—you define what your flake outputs are supposed to look like.
Here is an example of what the outputs of a flake, extracted using that flake’s schemas, look like in FlakeHub:
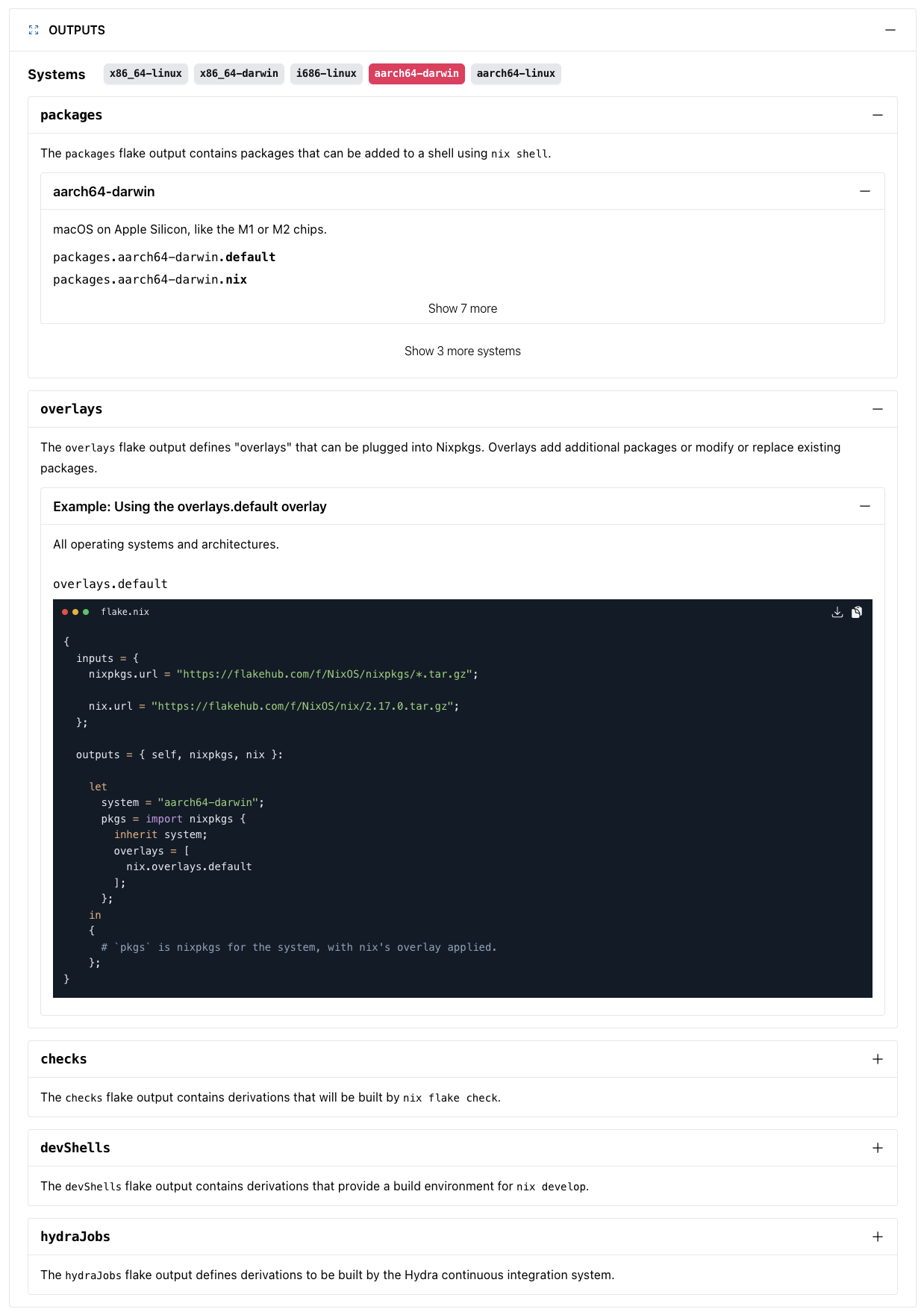
Using flake schemas
While you can define your own schema definition (see below), usually you would use schema definitions provided by others.
We provide a repository named flake-schemas with schemas for the most widely used flake outputs (the ones for which Nix has built-in support).
Declaring what schemas to use is straightforward: you just define a schemas output.
{ # `flake-schemas` is a flake that provides schemas for commonly used flake outputs, # like `packages` and `devShells`. inputs.flake-schemas.url = github:DeterminateSystems/flake-schemas;
# Another flake that provides schemas. inputs.other-schemas.url = ...;
outputs = { self, flake-schemas, other-schemas }: { # Tell Nix what schemas to use. schemas = flake-schemas.schemas // other-schemas.schemas;
# These flake outputs will now be checked using the schemas above. packages = ...; devShells = ...; };}Defining your own schemas
With schemas, we can now teach Nix about the lib output mentioned previously. Below is a flake that has a lib output.
Similar to lib in Nixpkgs, it has a nested structure (for example it provides a function lists.singleton).
The flake also has a schemas.lib attribute that tells Nix two things:
- How to list the contents of the
liboutput. - To check that every function name follows the camelCase naming convention.
{ outputs = { self }: {
schemas.lib = { version = 1; doc = '' The `lib` flake output defines Nix functions. ''; inventory = output: let recurse = attrs: { children = builtins.mapAttrs (attrName: attr: if builtins.isFunction attr then { # Tell `nix flake show` what this is. what = "library function"; # Make `nix flake check` enforce our naming convention. evalChecks.camelCase = builtins.match "^[a-z][a-zA-Z]*$" attrName == []; } else if builtins.isAttrs attr then # Recurse into nested sets of functions. recurse attr else throw "unsupported 'lib' type") attrs; }; in recurse output; };
lib.id = x: x; lib.const = x: y: x; lib.lists.singleton = x: [x]; #lib.ConcatStrings = ...; # disallowed };}With this schema, nix flake show can now show information about lib:
# nix flake showgit+file:///home/eelco/Determinate/flake-schemas/lib-test└───lib ├───const: library function ├───id: library function └───lists └───singleton: library functionWhile nix flake check will now complain if we add a function that violates the naming convention we defined:
# nix flake checkwarning: Evaluation check 'camelCase' of flake output attribute 'lib.ConcatStrings' failed.Find out more about how Determinate Systems is transforming the developer experience with Nix flakes
What schemas are not
Flake schemas are not a type system for Nix, since that would be a huge project.
They merely provide an interface that enables users to tell Nix how to enumerate and check flake outputs.
For instance, for a
Next steps
Flake schemas are new, and they’re a valuable expansion of the user experience of nix flake show and nix flake check.
Please take a look!
As future work, schemas will enable us to finally make flakes configurable in a discoverable way: flake schemas can return the configuration options supported by a flake output—for the nixosConfigurations output, for example, these would be all the NixOS options—and then the
Conclusion
Flake schemas solve a long-standing problem with flakes: the fact that Nix currently has built-in support for a only small set of output types, which made those outputs more equal than others. With schemas, all flake output types are on an equal footing.
